How to help a grieving friend
Nature's Symphony
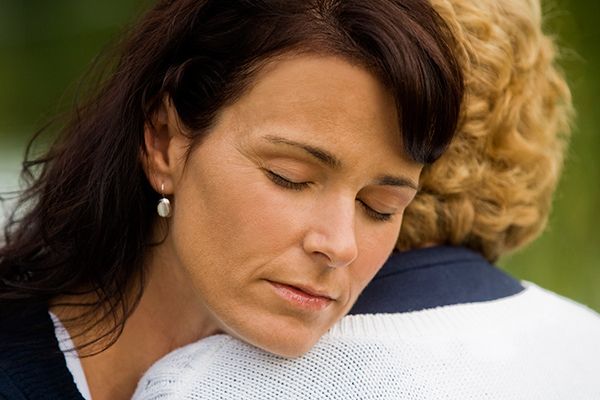
If one of your close friends has ever experienced a major loss, you know that watching somebody you care about suffer is, in itself, a type of suffering. Understand that there’s no way to solve all of your friend’s woes during this time. You can, however, offer support. Here are some ways you can be there for somebody you care about when they’ve lost somebody close to them.
Listen and acknowledge their feelings
Simply offering to listen to whatever your friend needs or wants to talk about can be a major benefit in his or her grieving process. Your friend may want to tell stories about his lost loved one or the events that led up to their passing. He may also want to talk about how he’s feeling or dealing with the loss. One of the best things you can do is tell your friend that you’re available to listen whenever he needs to talk, and then really listen when that time comes. It can be tempting to interject with advice during conversations like these, but your friend is probably already overwhelmed. Just being there to listen for the time being may be more comforting.
Offer to help, and be specific
You’re a great friend for wanting to help, but saying something as vague as, “Let me know if you need anything,” is often less helpful than making a specific offer. After all, your grieving friend may be so overwhelmed that he doesn’t know exactly what he needs or how you can be most helpful. So consider making a suggestion. “I’m heading to the store, why don’t I pick up some groceries for you?” “The grass seems to be growing really fast right now. How about I mow your lawn for the next few weeks?” These seemingly small gestures will allow your friend to focus on other tasks and recovery.
What not to say to someone who is grieving
Sometimes when we’re trying to be comforting during a difficult time, we accidentally say something that isn’t productive to a mourner’s healing process. Here are some phrases that are probably best to avoid.
- “I know how you feel.” This phrase, while filled with good intentions, can feel dismissive to a griever. In fact, although you may have experienced a loss in the past, you have no way of knowing exactly how your friend is feeling. It is better to acknowledge that his or her situation is unique.
- “She is in a better place.” Whether or not this statement is actually true, it tends not to make the griever feel better. After a loss, we usually deeply miss the departed, and we don’t want to imagine that their happy place isn’t right next to us.
- “There is a reason for everything.” Telling a mourner that their great loss was an intentional part of a plan can actually be somewhat hurtful.
- “Don’t cry/be strong.” It’s perfectly normal, even healthy, for your friend to allow herself to truly feel the full range of emotions that accompany a loss. Avoid the inclination to tell her to feel differently or act as though she does.
- “It was his time.” Again, although intended to be comforting, this statement can be the exact opposite. In the case of unexpected deaths and tragedies, stating that it was somebody’s “time” is not a sensitive response to their grieving loved ones.
Listen, offer to do something specific to help, and be there for your friend. They will always remember your comforting presence.